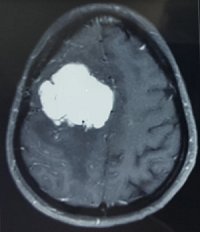
Meningiomas are a diverse set of tumors arising from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the central nervous system. Many meningiomas produce no symptoms throughout a person’s life, and if discovered, require no treatment other than periodic observation. Typically, symptomatic meningiomas are treated with either radiosurgery or conventional surgery.
Meningiomas are often benign tumors arising from the coverings of the brain and spinal cord. They arise from the arachnoid “cap” cells of the arachnoid villi in the meninges. They represent about one-third of all primary brain tumors and occur most frequently in middle-aged women. Meningiomas usually grow inward, causing pressure on the brain or spinal cord. They also can grow outward toward the skull, causing it to thicken. Most meningiomas are benign noncancerous and slow-growing tumors.